Plastic surgery allows to address the foot of diabetics preventively or to correct the complications of the disease. Thanks to the reconstruction of ulcers it is possible to avoid amputations and we will explain why.
Plastic surgery and diabetic foot
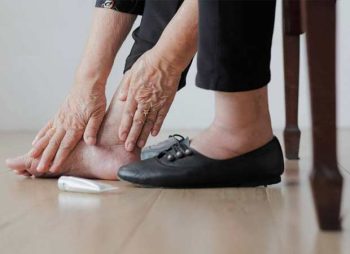
The appearance of ulcers on the feet of a diabetic patient is the result of a nerve injury called diabetic neuropathy. Consequently, the nerves are affected in their three components. On the one hand, at the sensory level, since there are alterations in the sensitivity of the foot, being unprotected and more loaded.
On the other hand, diabetic neuropathy produces alterations in the form of support of planting, which causes you to lose the normal way of walking. At the autonomous level, it is responsible for the appearance of dryness on the skin.
To prevent the appearance of diabetic foot, daily monitoring is necessary to prevent the development of these lesions. It is necessary to recognize existing deformities in order to treat them before ulcers form.
There are several ways to apply plastic surgery to diabetic foot. First, preventively, this technique can perform posterior tibial nerve desiccation to improve neuropathy in case patients have lost sensation.
On the other hand, it is important for the reconstruction of foot ulcers to avoid amputations. This requires a vascular and traumatological study, in addition to ruling out that there are infections in the bone. When there are healthy vessels and there is no infection, we can consider reconstruction so as not to amputate.
To proceed with the reconstruction, transplants of healthy and vascularized tissues are carried out from other locations of the body such as the thigh, which join arteries and veins of the feet. Without exquisite care of the intervened foot and proper control of the disease, ulcers will come out again in a short time.
Given the challenges of healing complicated wounds in patients with diabetes, use of plastic surgery techniques ranging from partial thickness skin grafts and local random flaps to muscle flaps and pedicles is essential.
The global impact of diabetic foot has made very clear the need for robust and durable surgical options to facilitate rapid closure of wounds.
Treatment of diabetic foot wound challenges the surgeon with multiple obstacles on the way to eventual wound closure. There are numerous options available and one must be familiar with each modality in order to select the best treatment for the patient. Surgeons must also ensure a thorough diagnosis and carefully consider a number of factors (patient age, vascular status, comorbidities, adherence, etc.) to determine the best course of treatment.
Plastic surgery techniques for soft tissue reconstruction have proven successful for long-term healing and stabilization. Accelerated healing of these complicated wounds not only improves the patient’s quality of life, but can also significantly reduce the healthcare costs associated with prolonged wound care. These techniques require meticulous perioperative planning.
The fundamental goals of plastic surgery techniques in wound closure have not changed since ancient times: preservation of form and function. A deep understanding of the gradual approach to the use of such procedures is imperative to obtain successful results.
Regardless of the approach you use, the main goal is to achieve a healthy, uninfected wound with adequate perfusion and biomechanical stability. Ultimately, you strive to achieve a plantigrade and functional foot without residual and recurrent ulcerative lesions.
Surgeons can perform concomitant bone reconstructive procedures to correct the underlying deformity and further promote foot stabilization for soft tissue reconstruction. In addition, proper discharge techniques, such as a complete cast, ferulization or external fixation with assistive devices, are vital to the durability of soft tissue reconstruction of soft tissue reconstruction.